Construction Materials: Mortars and Concrete
We aim at utilization of end-of-used products (fly ash, bottom ash) or industrial by-products (blast furnace slag) to be used for construction materials such as cement and concrete. This approach has several benefits:
-
It reduces the amount of incinerator by-products (bottom ash, fly ash) landfill.
-
It is substitution in clinker can reduce the use of “ordinary Portland Cement” (OPC) which is in fact a major contributor to global CO2 emission.
-
It helps preserving natural resources such e.g. minerals, natural sand.
We have shown that vitrified bottom ashes can serve for two purposes in mortars and clinkers. They can substitute OPC, and they can serve as a sand substitute in clinker as well. The experiments on the final mortar after 28 days show comparable values to the standard clinker if vitrified ashes are used up to 10 wt%.
Right) Effect of clinker substitution on the compressive strength of mortars over time.
The tests were conducted on mortars with 10%, 20%, and 30% of clinker (OPC) replace- ment by substituting: bottom ashes W1-C (vitrified bottom ash), W2-C (carbonized bottom ash), W2-W-C (carbonized and Ca(OH)2 washed bottom ash), blast furnace slag and calcite
Left) Effect of sand substitution on the compressive strength of mortars over time.
The tests were conducted on mortars with 10%, 20%, and 30% of sand substitution by vitrified bottom ash (W1-S).
Bottom Ash Utilization in Concrete
Activity in cooperation with: Buzzi Unicem
(www.buzziunicem.i) ![]()
In this activity, municipal waste incinerator bottom ashes were vitrified at 1450 °C without adding any vitrifying agent then ground and sieved to different granulometry (ranging from 50 lm to 20 mm), and used as filler, sand, or aggregate for concrete. Different tests such as slump tests (UNI 9418), alkali-silica reactivity (UNI 8520/22 and ASTM C 298), and compression strength tests (UNI 6132, 6132/72, 6686/72) were conducted on the final concrete. The results confirm the suitability of vitrified bottom in concrete if used as an aggregate substitution up to 20 wt% , and as cement substitution up to 75 wt%.
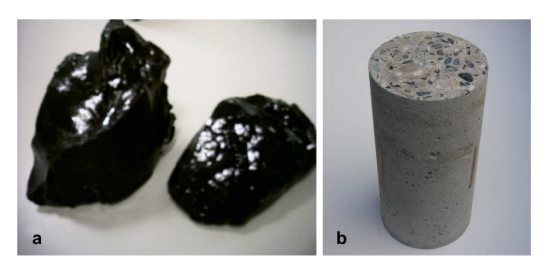
-
Vitrified bottom ashes (VBA); (b) concrete with VBA as aggregate.
Keywords: circular economy; mortar; bottom ash; concrete ; OPC
Contact(s): Elham Sharifikolouei, Milena Salvo, Monica Ferraris (monica.ferraris@polito.it)
Reference: [Ferraris et al, 2009] D.O.I : 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.07.014